Examples of general purpose applications:

Word Processing Software: This software enables the users to create and edit documents. The most popular examples of this type of software are MS-Word, WordPad, Notepad and some other text editors.
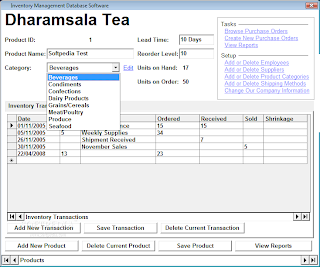
Database Software: Database is a structured collection of data. A computer database relies on database software to organize the data and enable the database users to achieve database operations. Database software allows the users to store and retrieve data from databases. Examples are Oracle, MSAccess, etc.

Spreadsheet Software: Excel, Lotus 1-2-3 and Apple Numbers are some examples of spreadsheet software. Spreadsheet software allows users to perform calculations. They simulate paper worksheets by displaying multiple cells that make up a grid.
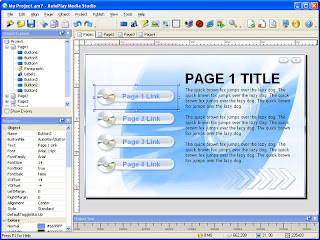
Multimedia Software: They allow the users to create and play audio and video media. They are capable of playing media files. Audio converters, players, burners, video encoders and decoders are some forms of multimedia software. Examples of this type of software include Real Player and Media Player.

Presentation Software: The software that is used to display information in the form of a slide show is known as presentation software. This type of software includes three functions, namely, editing that allows insertion and formatting of text, methods to include graphics in the text and a functionality of executing the slide shows. Microsoft PowerPoint is the best example of presentation software.
Function-specific application software is very specific in its use. Engineering programs often fall under this category - there is a program that does slope stability analysis and nothing else, for instance. Special purpose software may also be created in house and tailored to the specific needs of the company.
Examples of function-specific application software:

Engineering application software: Visual Basics

Business application software: Point of Sales (POS)

Accounting application software: User Business System (UBS accounting)
In general, special purpose software is intended to perform a very specific function, while general purpose software is intended to perform a broader class of functions.
No comments:
Post a Comment